Do you want to transfer files across Amazon S3 quickly & efficiently? If so, look no further than Replication. With a few simple steps, you can easily replicate objects across Amazon S3 buckets – even if they belong to another AWS account. This guide provides complete information on how replication works within an S3 environment and step-by-step instructions for easily configuring file transfers. So whether your goal is to copy data between two personal accounts or move documents from one company’s storage system to another, replication makes it a breeze!
What is S3 Replication, and why should you use it
Amazon S3 Replication is an excellent tool for businesses looking for a comprehensive solution to data replication. It enables quick and easy synchronization of objects across multiple buckets, regardless of ownership. This makes it an ideal choice for organizations that must comply with their data policy while optimizing latency and performance by storing the objects in different regions. In addition, when utilized efficiently, Replication can aggregate logs or take periodic backups to ensure redundancy and resilience against potential disaster scenarios.
How to set up Amazon S3 replication
You can create a replication configuration in the AWS console with simple steps. AWS CLI and Terraform provide additional automated solutions for creating and managing a replication configuration. AWS SDK also provides libraries with an Aws account to manage replication without any extra setup or manual process programmatically. With just a few clicks, Amazon S3 Replication gives you the confidence that your data is securely stored across multiple intelligent storage locations.
Benefits of using S3 replication
S3 replication can provide businesses with a secure Disaster Recovery (DR) solution. By replicating data stored on Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) across multiple AWS regions, companies ensure their data is readily available in an emergency or disaster. S3 also provides low latency as objects are automatically and synchronously stored across multiple availability zones in the same region. In other words, businesses are better protected against sudden data unavailability since they can easily and quickly access their replicated data from another region or provider should an emergency arise. This makes S3 replication a highly beneficial tool regarding Disaster Recovery planning.
Troubleshooting common issues with S3 replication
S3 replication is a handy and powerful tool for ensuring data security and system redundancy. However, to successfully Troubleshoot common problems with S3 replication, it’s necessary to understand the various components involved.
This profound analysis will discuss common S3 replication troubleshooting issues and potential solutions.
Replication lag: Replication lag is a common issue where data replication from the source bucket to the destination bucket is delayed. This can happen for various reasons, including network latency, insufficient bandwidth, or misconfiguration of replication rules.
Potential solutions: To troubleshoot replication lag, you can use the Amazon S3 Replication Time Control feature to monitor the replication status and identify delays. You can also optimize the network connectivity between the source and destination buckets or adjust the replication rules to ensure the replication frequency suits your needs.
Replication failures: Occur when an error in the replication process prevents data from being replicated from the source bucket to the destination bucket. This can happen for various reasons, such as network connectivity issues, insufficient permissions, or resource constraints.
Potential solutions: To troubleshoot replication failures, you can check the S3 replication status and logs to identify the error messages. You can also verify that the replication rules are configured correctly and that the necessary permissions are set up.
Data consistency issues: Can arise when the source and destination buckets have different versions of the same object or when objects are deleted from the source bucket before they are replicated in the destination bucket.
Potential solutions: To troubleshoot data consistency issues, you can use versioning to keep track of object versions and ensure that objects are replicated in the correct order. You can also use S3 event notifications to monitor object changes and trigger replication rules accordingly.
Insufficient permissions: This can prevent data from being replicated from the source bucket to the destination bucket. This can happen when the replication user does not have the necessary permissions to access the source or destination bucket.
Potential solutions: To troubleshoot insufficient permissions, you can verify that the replication user has the necessary permissions to access the source and destination buckets. You can also use AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) to grant appropriate permissions to the replication user.
Replication costs: This can become an issue when the size of the data being replicated is large or when the replication frequency is high.
Potential solutions: To troubleshoot replication costs, you can optimize the replication rules to ensure that only necessary data is replicated or adjust the replication frequency to reduce costs. You can also use Amazon S3 Intelligent Tiering to automatically move data between storage classes based on access patterns and cost.
By understanding the common issues and potential solutions, you can ensure that your data replication process runs smoothly and efficiently. The key is to monitor the replication status regularly, verify that the replication rules are configured correctly, and optimize the replication settings to suit your needs.
Best practices for setting up S3 replication
Setting up S3 replication is an essential best practice for meeting data requirements. Following the recommended strategy for setting up S3 replication will provide the necessary tools to ensure files are replicated in a cost-effective and organized manner.
Start by deciding what data needs to be replicated. This should include determining which buckets must be set up, ensuring they are separate from the source bucket, and configuring access control lists or AWS Identity and Access Management roles accordingly.
Depending on your specific needs, you should also configure one of the three types of S3 replication available: cross-region, same region, or cross-account. Replication can be automatized with S3 events, triggering other operations when changes occur.
For added security, you can add additional layers of encryption since any unauthorized access can compromise replicated data resources. Following these best practices for setting up S3 replication ensures you meet all security and performance requirements while controlling costs.
Advanced features of Amazon S3 Replication
Amazon S3 can copy objects from one S3 bucket to another using S3 Replication. An advanced feature of S3 Replication is S3 Replication Time Control (S3 RTC) which allows automatic, schedule-based replication of S3 objects within and across regions.
Administrators can use S3 RTC to automate the replication of buckets depending on their workloads, helping minimize latency and improve performance. By enabling S3 RTC, users can easily change replication schedules with a few clicks while avoiding the hassle of managing complex application configurations or sophisticated scripting solutions.
Encrypted Objects
When replicating encrypted objects, there are a few things to remember.
Firstly, S3 replication can replicate server-side encryption (SSE-S3, SSE-C, SSE-KMS) and client-side encryption. If you are using server-side encryption, the replication process will copy the encrypted object as is to the destination bucket or region. This means that the encryption key used to encrypt the object will also be replicated to the destination, and the object will remain encrypted during the entire replication process.
If you are using client-side encryption, where you encrypt the object before uploading it to S3, the replication process will also replicate the encrypted object as is to the destination. This means that the destination bucket or region will receive the encrypted object and cannot access its contents unless they have the encryption key to encrypt it.
If you use SSE-KMS encryption, you must ensure that the destination bucket or region can access the same KMS key to encrypt the object in the source bucket or region. The replication process will fail if the destination cannot access the key.
Overall, AWS S3 replication works seamlessly for encrypted objects if you take the necessary precautions to ensure the encryption keys are available in both the source and destination buckets or regions.
How to Learn More
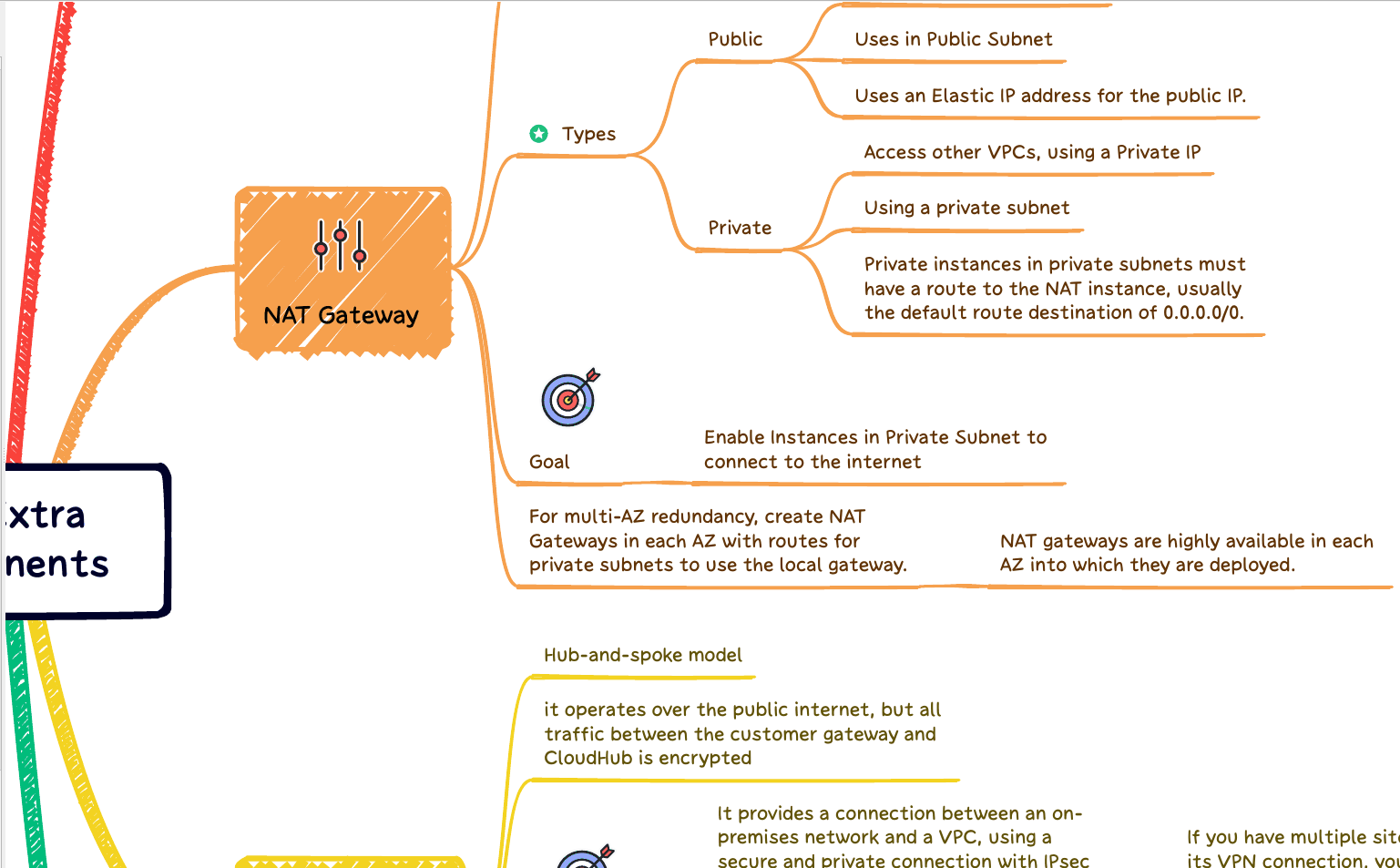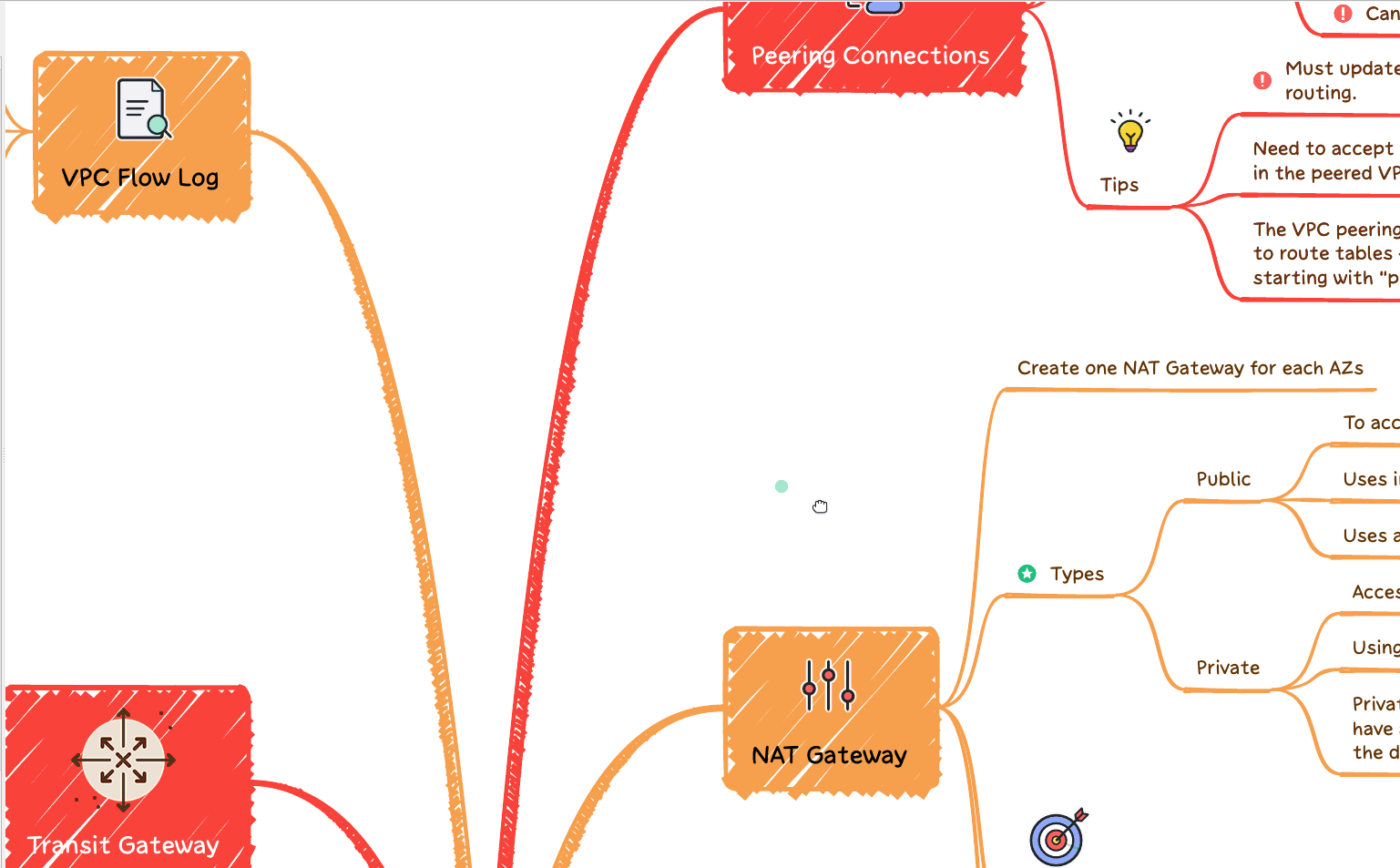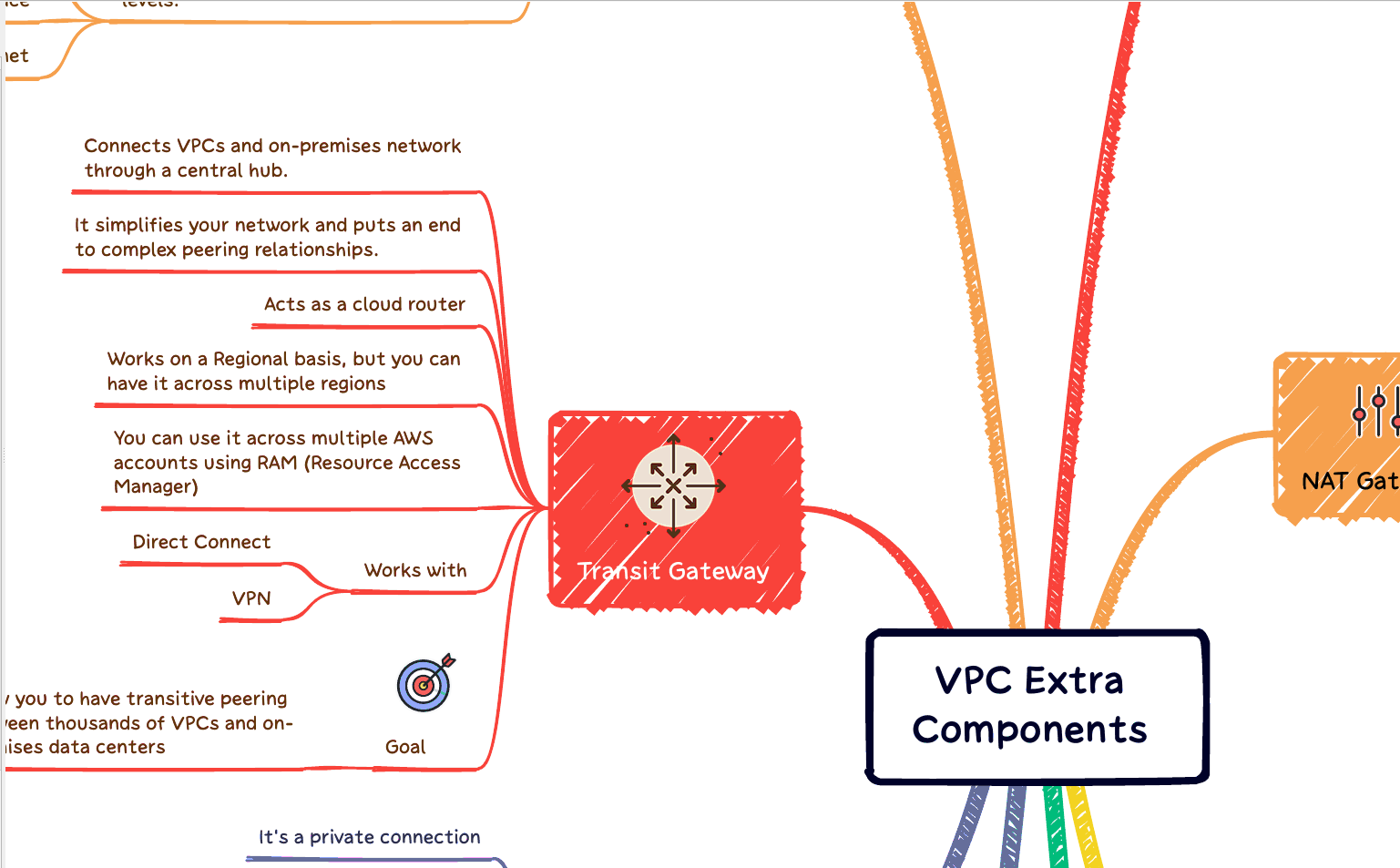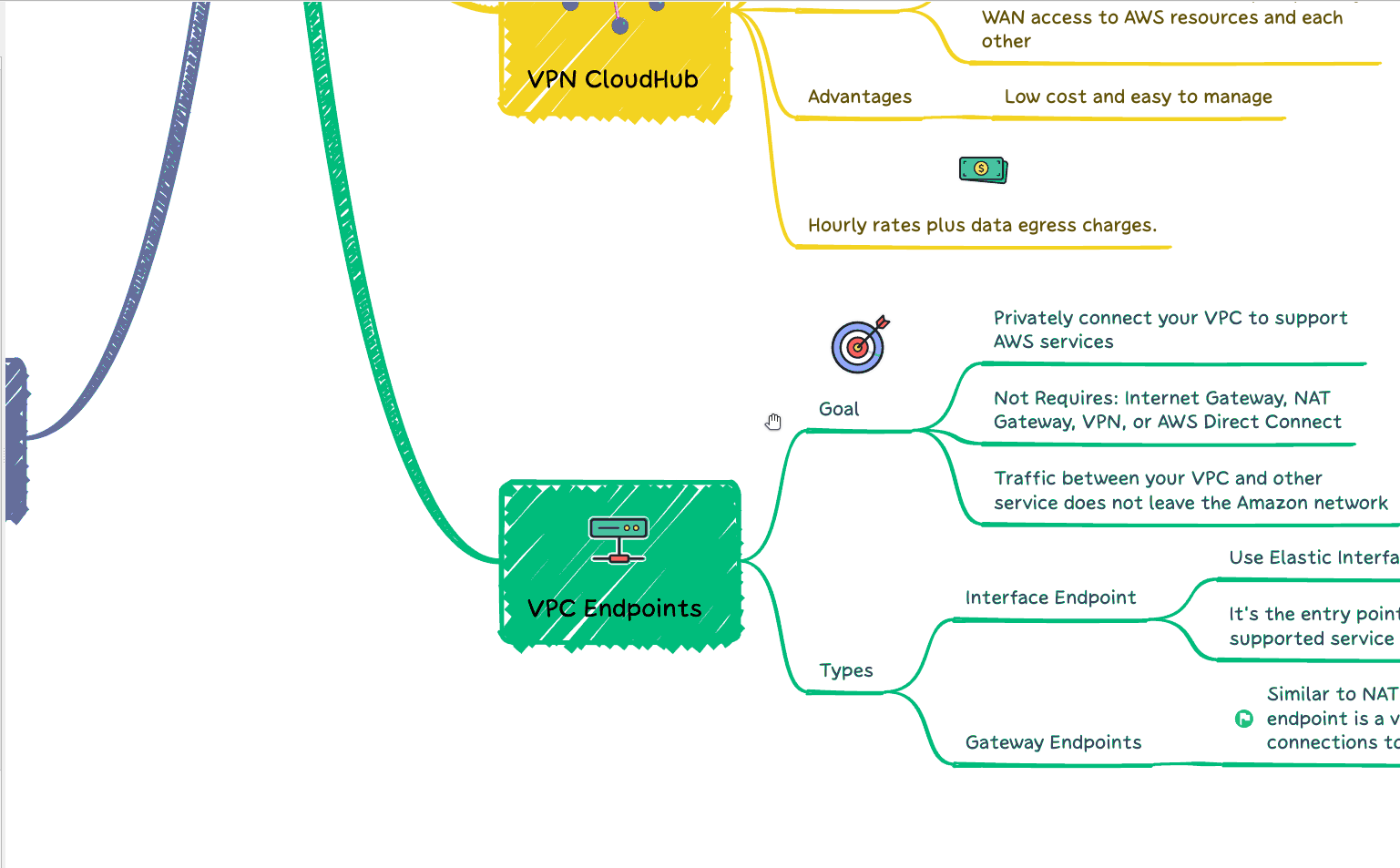
Are you looking to rapidly up your AWS expertise and become a more skilled user of the world’s most in-demand cloud computing platform? Our comprehensive AWS Learning Kit is precisely what you need! With 20 Mind Maps and 260 Questions with Answers included in this PDF guide, our resource will help equip you with invaluable knowledge about AWS without spending hours wading through online tutorials or taking pricey classes.
Mind Maps, with their captivating visual illustrations, empower your understanding of the key concepts related to Amazon Web Services. Not only do these visuals make learning simple for students, but they also give them an effective way to review information quickly. All maps have been carefully crafted by experienced professionals who are well-versed in using AWS technologies.
Our comprehensive, expertly crafted material is the ideal resource for anyone seeking to expand their AWS knowledge enjoyably and interactively rapidly. With its engaging visuals, and efficient questions and answers, our content ensures you will become a master of Amazon Web Services in no time! So if you want to increase your understanding of AWS with ease quickly – look no further than our amazing tool here. Get started now and take your learning experience up a notch today!
Conclusion
In conclusion, Amazon S3 replication offers an invaluable suite of capabilities to the business sector. It provides redundancy, scalability, and peace of mind for companies who know their data is securely stored in multiple regions. In addition, its advanced features, like replica placement and versioning, reduce the margin of any loss and make life a little easier.
Setting up S3 replication can be tricky, with complicated configuration rules and requirements, but following best practice tips helps ensure a smooth rollout.
With troubleshooting advice and comprehensive online documentation, businesses can access powerful data-sharing software without relying on complex development systems. Though setting up S3 replication requires understanding its capabilities and expectations, the rewards are worth it in terms of performance gains, versatility, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
To learn more about how your business can benefit from S3 Replication, download our AWS material for free!